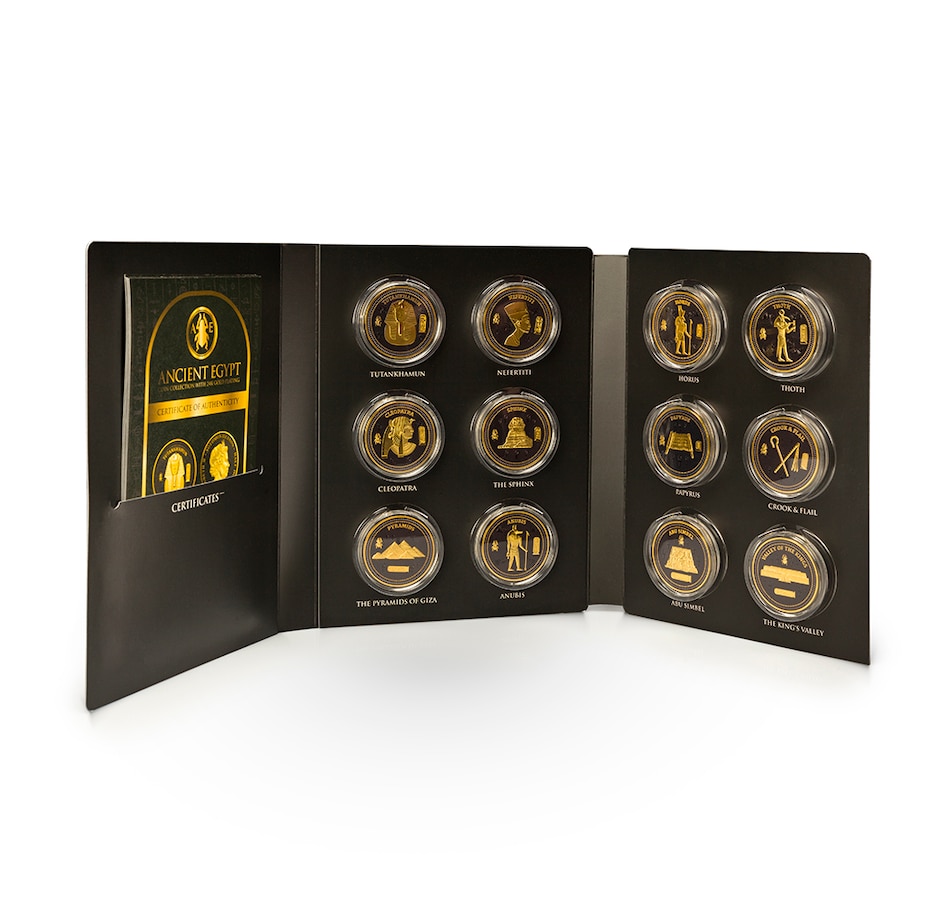
2022 Ancient Egypt 12-Coin Half-Dollar Collection
Free Shipping
Product Overview
Each motif features a scarab as a collection privy mark, the motif's title in hieroglyphic writing and well-known ancient Egyptian symbols as background elements. The coins are all part of a limited edition and are issued by Solomon Islands with a half-dollar nominal face value.
Tutankhamun (1332–1323 BCE)
Tutankhamun was the last ancient Egyptian pharaoh of his family to rule during the 18th Dynasty during the New Kingdom of Egyptian history. His father was the Pharaoh Akhenaten and his mother was Nefertiti. He came to the throne at the age of eight years and was married to Ankhesenamun, his half-sister. He was physically disabled with a deformity of his left foot along with bone necrosis that required the use of a cane, several of which were found in his tomb, as well as body armour and bows, since he had been trained in archery. Tutankhamun restored the ancient Egyptian religion after its dissolution by his father, enriched and endowed the priestly orders of two important cults and began restoring old monuments damaged during the previous Amama period.
For more than 3,000 years, Tutankhamun lay undisturbed until on a late November day in 1922 when British archaeologist Howard Carter and his sponsor Lord Carnarvon entered the tomb of the "Boy Pharaoh." There they discovered the tomb miraculously intact. The Egyptologists found thousands of artifacts, the most splendid of which was a stone sarcophagus containing three coffins nested within each other. Inside the final coffin, which was made out of solid gold, was Tutankhamun's mummy upon which rested a magnificent life-size gold mask of "King Tut" himself. Today, the Mask of Tutankhamun is one of the world's most recognizable works of art and arguably the most prominent symbol of ancient Egypt.
Cleopatra (69–30 BCE)
She was the last active ruler of the Ptolemic Kingdom of Egypt, nominally survived as pharaoh by her son Caesarion. She wanted to consolidate and expand her empire, but was unable to achieve this goal against the power of Rome. As a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian Greek general and companion of Alexander the Great. After the death of Cleopatra, Egypt became a province of the Roman Empire, marking the end of the Hellenistic period that lasted since the reign of Alexander (336 BC–323 BC).
Nefertiti (1370–1330 BC)
She was an Egyptian Queen and the great royal wife of Akhenaten, an Egyptian pharaoh. She had many titles during her lifetime, including Hereditary Princess, Great of Praises, Lady of Grace, Sweet of Love, Lady of the Two Lands, Main King's wife, and Mistress of Upper and Lower Egypt. Nefertiti and her husband were known for a religious revolution in which they worshipped only one god: Aten or the Sun Disc. With her husband, she reigned at the wealthiest period of ancient Egyptian history. After her husband passed into the afterlife, she ruled the realm briefly, till her son Tutankhamun ascended the throne.
Thoth
Thoth is considered the secretary of the gods and the inventor of the hieroglyphs. He is also the god of magic, the moon, science, wisdom, and the calendar.
Anubis
Anubis is an ancient deity to whom prayers for survival of the deceased in the afterlife were addressed during the early Old Kingdom, before Osiris rose to prominence as the god of the dead. Anubis continued to assist in the judgement of the dead and accompanied the deceased to the throne of Osiris for the ritual of weighing the heart. Anubis was depicted as a jackal or as a man with the head of a jackal. Priests who prepared bodies for burial and conducted burial ceremonies impersonated the god by wearing jackal masks. Since jackals were common scavengers in Egyptian burial sites, the honouring of Anubis in this guise represented a way of protecting the dead from grave scavenging.
Horus
God of the sky, Horus advanced to the god of war and war leader, which gave rise to the belief that the pharaoh was his earthly embodiment.
Abu Simbel
Abu Simbel are two massive rock-cut temples in the village of Abu Simbel in Upper Egypt. They are situated on the western bank of Lake Nasser. The twin temples were originally carved out of the mountainside in the 13th century BCE, during the 19th Dynasty reign of the Pharaoh Ramesses II. They serve as a lasting monument to the king Ramesses II. His wife Nefertari and children can be seen in smaller figures by his feet, and were considered to be of lesser importance and not given the same position of scale. This commemorates his victory at the Battle of Kadesh. Their huge external rock relief figures have become iconic.
Valley of the Kings
This is a necropolis where 64 tombs and pits have been found.
The Sphinx
This mythical creature had the head of a human and the body of a lion. Sphinxes are seen as benevolent but also having ferocious strength, and are also seen in pairs as guardians, often flanking the entrances to temples.
The Pyramids
The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures; around 138 such structures have been identified so far. Most of the pyramids were built as tombs for the pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods. The most famous Egyptian pyramids are those found at Giza in the outskirts of Cairo. Several of the Giza pyramids are counted among the largest structures ever built. The Pyramid of Khufu at Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid, and is the only one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World still in existence.
Crooks and Flail
These are the most famous symbols of pharaonic power. The crook is called heka in ancient Egypt, and means "to rule". The flail was called nechech, and is a short crook with three hanging strands, that stood for the fertility of the land.
Papyrus
The ancient Egyptians used the stem of the papyrus plant to make sails, cloth, mats, cords, and above all, paper. Paper made from papyrus was the main writing material in ancient Egypt, later adopted by the Greeks and also used extensively in the Roman Empire.
• Mintage: 15,000 each except King Tut (30,000)
• Diameter: 45 mm each
Includes:
• 2022 Ancient Egypt 12-Coin Half-Dollar Set
Warranty Information:
This product comes with a 30-day warranty through TSC.